Whether you’re a graphic designer, photographer, or anyone working with visuals, it’s important to understand the distinction between these two color spaces.
In this article, we’ll take a detailed look at RGB and CMYK, focusing on their characteristics, applications, and key differences.
What is RGB
RGB is an additive color model. It stands for red, green, and blue, which are the primary colors of light. In this color model, the varying intensities of these three colors combine to create a wide range of hues, with 16 million colors to choose from. The values for RGB range from 0 to 255, giving 256 levels for each color (red, green, and blue).
When all three primary colors are absent, we get black (R: 0 G: 0 B: 0), and when they are at their maximum intensity, we get white (R: 255 G: 255 B: 255).

When should you use RGB?
RGB color mode is ideal for any digital media that emits or reflects light. It’s perfect for creating vivid visuals on screen and is an excellent choice for content involving mobile devices and computer screens.
Here are some common examples of RGB color mode applications in everyday life:
- Web design
- Digital advertising
- Video
- Video games
- Digital signage
- Images in social media
What is CMYK
CMYK stands for cyan, magenta, yellow, and the key color (black). It is a subtractive color model used in the printing process. The “K” in CMYK stands for the primary color, which is black. When all colors are combined at full intensity, we get a rich, deep black.

Unlike RGB, which starts with black and adds light, CMYK starts with white and subtracts color to create different hues. By combining these four ink colors in varying intensities, we can produce the full spectrum of colors required for printing.
CMYK values are expressed in percentages, for example, C=50, M=20, Y=50, K=20. This means that the cyan ink intensity is 50%, the magenta ink intensity is 20%, the yellow ink intensity is 50%, and the black ink intensity is 20%.
When should you use CMYK?
The CMYK color model accurately reproduces colors in printing, making it the ideal choice for any print project. The four colors of CMYK are also the most commonly used ink colors in printers.
Here are common examples of CMYK color model applications in daily life:
- Business cards
- Flyers and brochures
- Posters
- Magazines
- Product packaging
- Greeting cards
- T-shirts
Key Differences Between RGB and CMYK
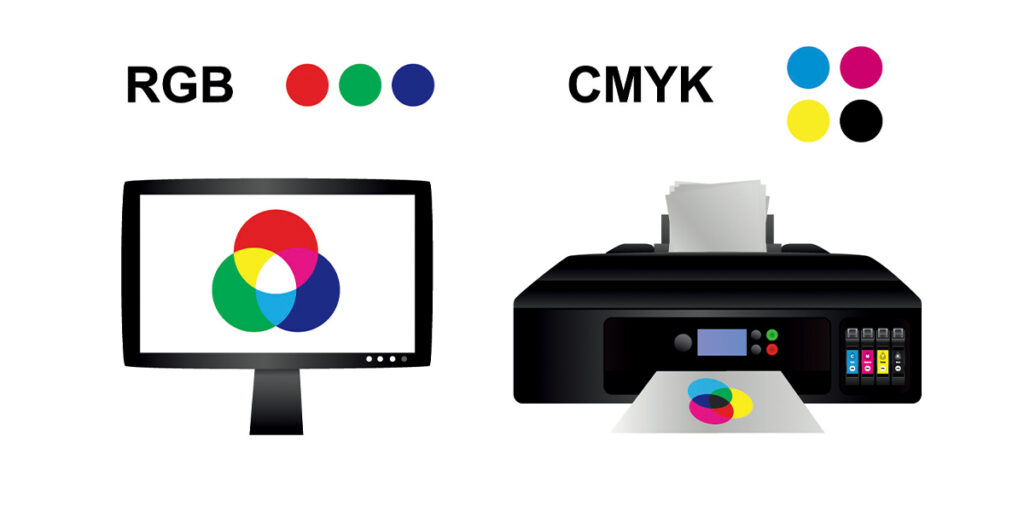

Understanding the key differences between RGB and CMYK is crucial for maintaining consistent and accurate color representation across various media. Here are the main differences:
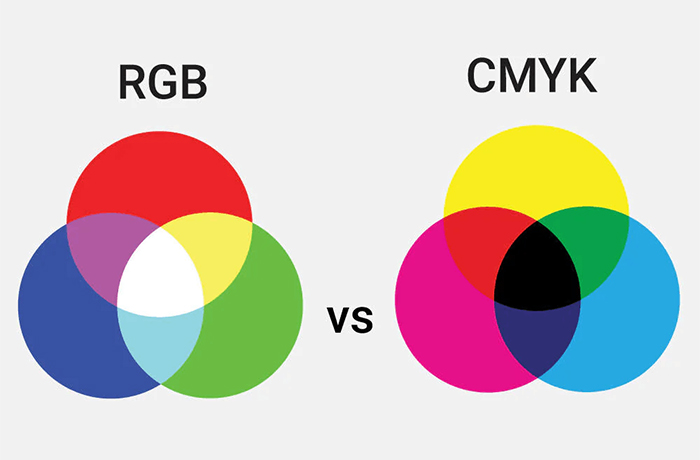
Color representation: RGB represents color using light, while CMYK represents color using ink. This fundamental distinction leads to variations in color range and intensity between the two models.
Color gamut: CMYK has a value range of 4 x 100, while RGB has a value range of 3 x 256. RGB has a broader color gamut, allowing it to display a wider range of vibrant colors compared to CMYK.
Additive vs. Subtractive: RGB follows an additive color model, where colors are combined to create lighter shades. In contrast, CMYK follows a subtractive color model, where colors are subtracted to achieve darker tones.
The more colors you add in CMYK mode, the darker the result becomes. The more colors you add in RGB mode, the lighter the result becomes.
Color mode application: RGB is primarily used for digital display, while CMYK is used for printing. Due to variations in color spaces, colors that appear vivid on a screen may appear dull or altered in print.

File format: RGB images are commonly saved in formats like JPEG, PNG, and GIF, while CMYK images are saved in formats such as TIFF or EPS.
Related article: Convert an image to another color mode
Conversion between RGB and CMYK
When transferring a design from digital to print media, it may be necessary to convert colors between RGB and CMYK, and vice versa. While it’s not always possible to get an exact match due to differences in color range, there are tools and techniques that can help with the conversion process.
Many graphic design software options, like Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Illustrator, and CorelDRAW, offer features to convert colors between RGB and CMYK. These programs provide settings for color management, allowing designers to preview and adjust how colors will look in different color spaces. When converting from RGB to CMYK, it’s important to review and fine-tune colors to ensure they remain visually appealing and consistent.
Application of RGB and CMYK in different industries
RGB and CMYK find applications in different industries, each serving a specific purpose. Here are some examples:
Graphic Design: Graphic designers use RGB to create digital artwork, web design, and visual content for online platforms.
Photography: Photographers use RGB when editing and enhancing digital photos for online presentations or digital portfolios.
Printing and Publishing: Printers, publishers, and advertisers rely on CMYK for accurate color representation in printed materials.
Branding and Packaging: The CMYK color space is crucial for maintaining consistent branding colors and ensuring accurate packaging design.
As technology advances, new color models and techniques are constantly being developed. These advancements aim to bridge the gap between RGB and CMYK, enabling more accurate color matching between digital displays and print. Such developments have the potential to revolutionize color reproduction across industries and enhance the overall visual experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between RGB and CMYK is crucial for individuals working with color in digital and print media. RGB is well-suited for digital displays, offering a broad range of vibrant colors, while CMYK is preferred for print media, ensuring accurate color reproduction. By knowing when to use each color model and how to transition between them, designers can create visually appealing and consistent content across various media.
Our mockup generator supports uploading designs in RGB color mode. When we print, we’ll use both RGB and CMYK color modes for different products to make sure the final product looks its best.

0 Comments