Each technology provides distinct advantages that cater to various requirements. Therefore, comprehending the disparities, merits, and suitable applications of screen printing and embroidery is crucial for making a well-informed choice.
Screen printing
Screen printing is frequently employed for large orders and is particularly common when printing T-shirts and hoodies.
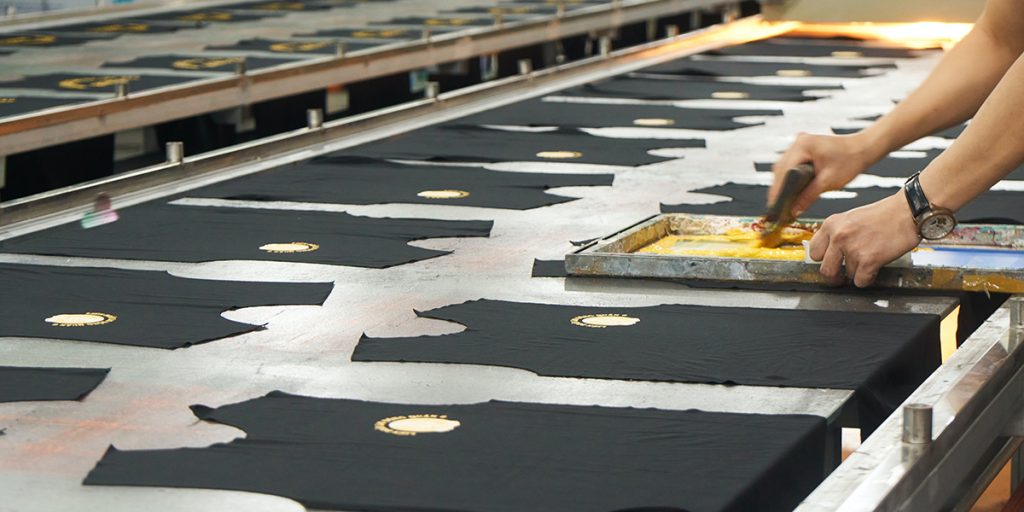

What is screen printing?
Screen printing, also known as silkscreen, is a method of printing that transfers ink to fabric through a stencil (or “screen”).
Each color in the design requires a separate screen, and each color must be cured before applying another.
How does screen printing work?

1. Creating the design
The desired design is printed onto a clear acetate film, which will serve as the stencil.
2. Making the screen
A fine mesh screen (usually silk, polyester, or nylon) is tightly stretched over a frame (typically wood or aluminum), and a photosensitive emulsion is applied to the screen.
3. UV exposure
The acetate sheet with the design is placed over the emulsion-coated screen, and the entire screen is exposed to UV light to dry the photosensitive emulsion.
4. Washing off the unhardened emulsion
Carefully rinse off any unhardened emulsion with water, removing the soft emulsion and leaving a clear imprint of the design on the screen.
5. Preparing to print
Place the screen on the press and position the item or garment flat underneath.
6. Inking
Apply ink to the top of the screen and use a scraper to force the ink through the mesh, transferring the ink through the screen and onto the fabric.
7. Curing
After printing, the ink must be cured or dried, which can be accomplished through air drying, heat curing (using a conveyor dryer or heat press), or UV curing.
If the design involves multiple colors, each color requires a separate screen and the process is repeated.
8. Cleaning
The screen can be reused by cleaning off the emulsion with a cleaning solution after each use.
Embroidery
Embroidery serves as a method to embellish clothing. While traditionally known for embroidered patches, it has also evolved into a fashion-forward printing technique.
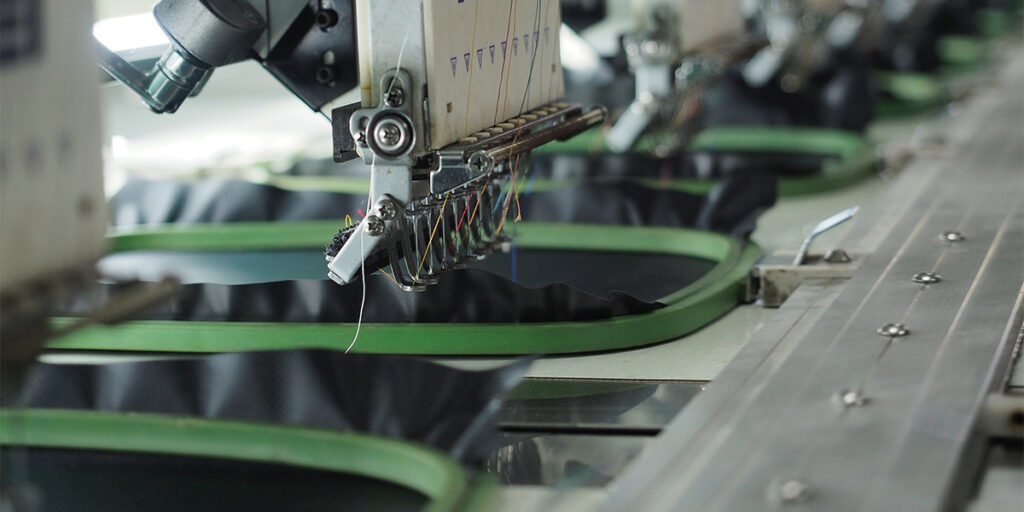

What is embroidery?
Embroidery is a technique used to embellish fabric using needle and thread. It involves sewing thread into the fabric to create textured designs, often resulting in a delicate and professional appearance.
Originally a handcraft, embroidery has evolved in the world of print-on-demand to be primarily executed by machines.
How does embroidery work?
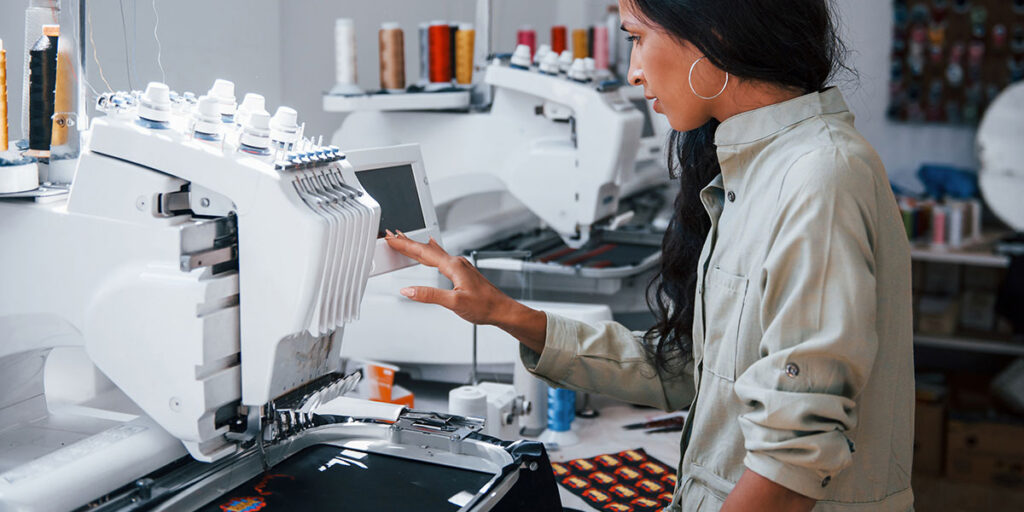

1. Creating the design
Special software is utilized to generate the desired embroidery pattern. This involves plotting the trajectory and determining the number of stitches permissible for the needle and thread, converting it into a format compatible with the embroidery machine.
2. Selecting needle and thread colors
Typically, embroidery machines can handle up to 16 colors, but they can only use 6 colors at a time. Therefore, the maximum number of colors that can be used in a pattern is 6.
3. Hooping
Different products like hats and T-shirts require specific hooping tools to secure them properly during embroidery.
4. Initiating Embroidery
Once the product is properly hooped, the embroidery machine can commence the stitching process.If your design exceeds 6 colors, attempting a second embroidery may result in alignment challenges and compromise the original pattern, hence it is not recommended.
Key differences between screen printing and embroidery
Cost
Screen printing costs vary depending on the number of colors used because each color requires separate stencils and screens. Initially, screen printing can be costly for small print runs, but the per-unit cost decreases as the quantity increases.
In contrast, embroidery costs remain consistent regardless of the number of colors used. It is economical for small areas. However, for larger embroidery areas, a larger and more expensive embroidery machine may be necessary, increasing production costs.

Suitability
Fabrics ideal for screen printing include smooth, flat, absorbent materials like cotton and cotton blends, which promote good ink adhesion and vibrant prints.
However, screen printing on stretchy or non-flat fabrics may lead to uneven ink application, cracking, or warping over time.
For embroidery, stable, medium-weight, smooth fabrics such as cotton, cotton blends, linen, wool, and polyester blends are recommended. These provide a sturdy foundation for clear and precise embroidery work without causing damage.
Avoid using fabrics treated with waterproof coatings, such as some high-performance outerwear or raincoats, for embroidery. These coatings can hinder the embroidery needle from penetrating the fabric properly, resulting in uneven or skipped stitches.
A skipped stitch occurs when the hook on the bobbin case fails to catch the thread from the needle at the right moment, resulting in a stitch that fails to form.
Durability
Screen printed designs may fade in color and appear cracked after multiple washes.
In contrast, embroidery is abrasion-resistant, and the design will not fade or break down after extensive washing or ironing.
Appearance
Screen printed designs will feature a smooth, flat surface, and their colors will appear especially vibrant on the fabric. It’s important to note that layering inks in screen printing can also create a subtly raised effect in your design.
Embroidery naturally adds texture through the stitching process. The thread is sewn into the fabric, producing a raised pattern and texture that is both visible and tangible.Additionally, embroidery techniques such as raised embroidery (utilizing padding under the stitches) or varying thread thicknesses can achieve a three-dimensional effect.
Conclusion
In summary, screen printing excels at producing large, colorful designs in high volumes for casual wear like custom T-shirts or hoodies. On the other hand, embroidery enhances professional attire with its durability and precise stitching.
Knowing these distinctions will assist you in selecting the method that aligns best with your brand objectives, budget considerations, and desired visual appeal. Whether you prioritize affordability, longevity, or intricate design, understanding these variations will empower you to make a well-informed choice.

0 Comments